
Potential of alternative scores to extend life expectancy The successor of MELD, an advanced scoring system, made by collaboration between Massachusetts General Hospital and IBM, called MELD-Plus was introduced in 2017. The etiology turned out to be relatively unimportant, and was also regarded as relatively subjective it was therefore removed from the score.
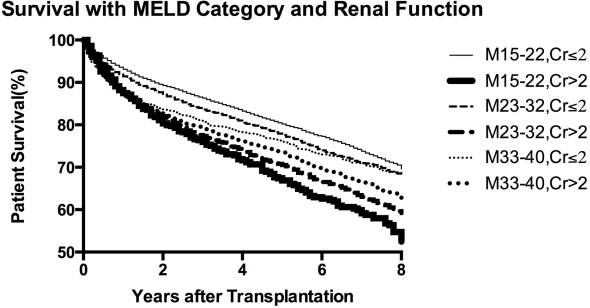
The score turned out to be predictive of prognosis in chronic liver disease in general, and-with some modifications-came to be applied as an objective tool in assigning need for a liver transplant.

The original version also included a variable based on the underlying etiology (cause) of the liver disease.
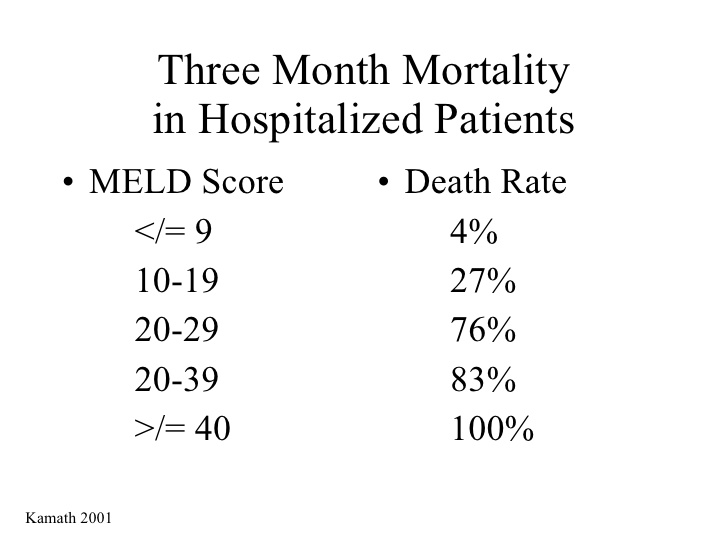
Meld score mortality series#
It was derived in a series of patients undergoing TIPS procedures. Patrick Kamath, and at that point was called the "Mayo End-stage Liver Disease" score. MELD was originally developed at the Mayo Clinic by Dr.
Meld score mortality how to#
The etiology of liver disease was subsequently removed from the model because it posed difficulties such as how to categorize patients with multiple causes of liver disease. if bilirubin is 0.8 a value of 1.0 is used) to prevent subtraction from any of the three factors, since the natural logarithm of a positive number below 1 (greater than 0 and less than 1) yields a negative value. Any value less than one is given a value of 1 (i.e.If the patient has been dialyzed twice within the last 7 days, then the value of serum creatinine should be 4.0 mg/dL.UNOS has made the following modifications to the score: MELD scores are reported as whole numbers, so the result of the equation above is rounded.

It is calculated according to the following formula: MELD = 3.78×ln + 11.2×ln + 9.57×ln + 6.43 MELD uses the patient's values for serum bilirubin, serum creatinine, and the international normalized ratio for prothrombin time (INR) to predict survival. This score is now used by the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) and Eurotransplant for prioritizing allocation of liver transplants instead of the older Child-Pugh score. It was initially developed to predict mortality within three months of surgery in patients who had undergone a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedure, and was subsequently found to be useful in determining prognosis and prioritizing for receipt of a liver transplant. The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease, or MELD, is a scoring system for assessing the severity of chronic liver disease. Scoring system for assessing the severity of chronic liver disease Model for End-Stage Liver DiseaseĪssess the severity of chronic liver disease


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
